Story of the Greeks - Helene Guerber |
The Blind Poet
Three or four centuries after the siege of Troy, there lived a poor old blind poet who wandered about from place to place, playing upon his lyre, and reciting wonderful verses which told about the adventures of the Greek heroes, and their great deeds during the Trojan War.
We are told that this old man, whose name was Homer, had not always been poor and blind, but that, having embarked by mistake upon a vessel manned by pirates, he not only had been robbed of all his wealth, and blinded, but had been left upon a lonely shore.
By some happy chance, poor blind Homer found his way to the inhabited parts of the country, where he soon won many friends. Instead of spending all his time in weeping over his troubles, Homer tried to think of some way in which he could earn his living, and at the same time give pleasure to others. He soon found such a way in telling the stories of the past to all who cared to listen to them.
 Homer. |
As the people in those days had no books, no schools, and no theaters, these stories seemed very wonderful. Little by little Homer turned them into verses so grand and beautiful that we admire them still; and these he recited, accompanying himself on a lyre, which he handled with much skill. As he wandered thus from place to place, old and young crowded around him to listen to his tales; and some young men were so struck by them that they followed him everywhere, until they too could repeat them. This was quite easy to do, because Homer had put them into the most beautiful and harmonious language the world has ever known. As soon as these young men had learned a few of the tales, they too began to travel from place to place, telling them to all they met; and thus Homer's verses became well known throughout all Greece.
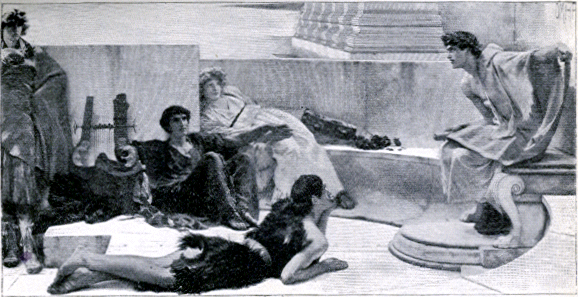 Telling Homer's Tales. |
The Greeks who could recite Homer's poems went next to the islands and Asia Minor, stopping at every place where Greek was spoken, to tell about the wrath of Achilles, the death of Patroclus, Hector, or old Priam, the burning of Troy, the wanderings of Ulysses, and the return of the Greeks. Other youths learned the poems; and so, although they were not written down for many a year, they were constantly recited and sung, and thus kept alive in the memory of the people.
As for Homer, their author, we know but little about him. We are told that he lived to be very old, and that although he was poor as long as he lived, and forced to earn his living by reciting his songs, he was greatly honored after his death.
His two great heroic poems—the Iliad, telling all about the Trojan War, and the Odyssey, relating how Ulysses sailed about for ten years on his way home from Troy—were finally written down, and kept so carefully that they can still be read to-day. Such was the admiration felt for these poems, that some years after Homer's death an attempt was made to find out more about him, and about the place where he was born.
Fifty cities claimed the honor of giving him birth; but, although it was never positively found out where he was born, most people thought the Island of Chios was his birthplace. The Greek towns, wishing to show how much they admired the works of Homer, used to send yearly gifts to this place, the native land of the grandest poet the world has ever known.